Download Image
5.37 MB
ID # 176
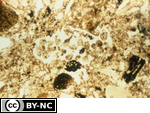
AggrotubuleFrom the Soil Micromorphology Slide Collection
STEM Standard addressed: ESS2E - Biogeology
Appropriate Grade Level(s)
- College-level
- Classroom Lectures
- Laboratory Activities
- Soil Microbiology
Micromorphological description Of slide: Loose infilling of undulating to smooth, fine meso excrement. Fecal pellets are weakly coalesced, more or less discrete and show no disintegration. Composition of pellets is largely mineral, similar to the adjacent matrix. Excrement is most likely that of Diptera (fly) larvae.
Data for the horizon
Horizon sampled: Ap
Depth sampled: 0-6 cm
Physical and chemical data available: pH = 5.9, org. C = 1 .76, N = 0.17%, exch. ca = 76.8%, exch. Mg = 19.3%, exch. K = 1 .03%, exch. Na = 0.34%, total exch. cap. (cmol (p +)/kg) = 1 4.5, clay = 19%, clay mineralogy = hydrous mica > kaolinite > smectite
Macromorphological description of horizon: Ap (0-1 5 cm): Dark grayish brown (IOYR 4/2. m) sandy loam to loam; compact, fragmented to massive; slightly firm to firm; abrupt smooth boundary.
Micromorphological description Of horizon : The upper 7 cm of the Ap horizon has a mixed matrigranoidic porphyric (85%) fabric (Brewer, 1976). The fabric is highly porous near the surface. At a depth of 7-14 cm the fabric arrangement is vughy porphyric. Voids (40%) are largely metavughs (8/10) of variable size, many are mammillated.
There are a few channels (1/10) of variable size throughout and a few skew planes (1/10) are in the lower section. Excrement features make up a significant portion of the fabric arrangement (20%). Strongly welded earthworm fecal pellets (9/10) are largely concentrated in aggrotubules. Collembola (springtail) fecal pellets (1 110) are found as infillings in channels and vughs. There are numerous (5-10%) meso and macro organic and sesquioxidic nodules throughout.
Data for thin section
Preparation of sample: Air dry
Impregnating medium: Epoxy
Thickness of section: 30 µm
Orientation of section: Vertical
Size of section: 5 X 7 cm
Soil Classification
U.S.: Typic Cryoboralf
F.A.O.: Albic Luvisol
Canada: Orthic Gray Luvisol
Elevation: 700 m above sea level
Topography and hill slope position: Level to undulating upper slope Parent material: Till
Soil climatic data and/or soil water balance: Subhumid moisture regime and cold soil temperature class
Vegetation: Cultivated field of barley (Hordeum vulqare)
Data for the horizon
Horizon sampled: Ap
Depth sampled: 0-6 cm
Physical and chemical data available: pH = 5.9, org. C = 1 .76, N = 0.17%, exch. ca = 76.8%, exch. Mg = 19.3%, exch. K = 1 .03%, exch. Na = 0.34%, total exch. cap. (cmol (p +)/kg) = 1 4.5, clay = 19%, clay mineralogy = hydrous mica > kaolinite > smectite
Macromorphological description of horizon: Ap (0-1 5 cm): Dark grayish brown (IOYR 4/2. m) sandy loam to loam; compact, fragmented to massive; slightly firm to firm; abrupt smooth boundary.
Micromorphological description Of horizon : The upper 7 cm of the Ap horizon has a mixed matrigranoidic porphyric (85%) fabric (Brewer, 1976). The fabric is highly porous near the surface. At a depth of 7-14 cm the fabric arrangement is vughy porphyric. Voids (40%) are largely metavughs (8/10) of variable size, many are mammillated.
There are a few channels (1/10) of variable size throughout and a few skew planes (1/10) are in the lower section. Excrement features make up a significant portion of the fabric arrangement (20%). Strongly welded earthworm fecal pellets (9/10) are largely concentrated in aggrotubules. Collembola (springtail) fecal pellets (1 110) are found as infillings in channels and vughs. There are numerous (5-10%) meso and macro organic and sesquioxidic nodules throughout.
Data for thin section
Preparation of sample: Air dry
Impregnating medium: Epoxy
Thickness of section: 30 µm
Orientation of section: Vertical
Size of section: 5 X 7 cm
Soil Classification
U.S.: Typic Cryoboralf
F.A.O.: Albic Luvisol
Canada: Orthic Gray Luvisol
Elevation: 700 m above sea level
Topography and hill slope position: Level to undulating upper slope Parent material: Till
Soil climatic data and/or soil water balance: Subhumid moisture regime and cold soil temperature class
Vegetation: Cultivated field of barley (Hordeum vulqare)
Method
Data for 35-mm slide
Frame length: 3.5 mm
Light mode: Plane polarized
Frame length: 3.5 mm
Light mode: Plane polarized
References
Brewer, R. 1976. Fabric and mineral analysis of soils. Krieger Publ. Co., Melbourne, Fl.
Bullock, P. , et al. 1985. Handbook of soil thin section description. Waine Research Publications, Wolverhampton, England. Pawluk, S. 1980. Micromorphological investigations of cultivated Gray Luvisols under different management practices. Can. J. Soil Sci. 60:731-745. Source - S. Pawluk
Slide BF32. Soil Science Society of America, 1993. A Reference Slide Collection for Soil Micromorphology. SSSA, Madison, WI.
Bullock, P. , et al. 1985. Handbook of soil thin section description. Waine Research Publications, Wolverhampton, England. Pawluk, S. 1980. Micromorphological investigations of cultivated Gray Luvisols under different management practices. Can. J. Soil Sci. 60:731-745. Source - S. Pawluk
Slide BF32. Soil Science Society of America, 1993. A Reference Slide Collection for Soil Micromorphology. SSSA, Madison, WI.
Peer Review: Yes
Credit this item to: SSSAMedia Date: 1993-01-01
Provided By: (SSSA) Soil Science Society of America
Latitude: 53.10999
Longitude: -114.47139479999998
Author(s)/Creator(s)
-
* Soil Science Society of America
SSSA
Submitted By: (SSSA) Soil Science Society of America
Keywords
- Biological Features
- Ap horizon
- micromorphology
- Aggrotubule
Comments
Please login to submit a comment.
Log In to your account
Already a member, certified, or existing customer?*
* Cookies must be accepted to log in.
Not sure if you have an account?
Check Your Email
Join Us!
Connect with members and access the information you need.
Learn more.
Ready to Join?
If you have an account, login on the left. Not sure if you have an account or need to create one? Check your email with the link above. We look forward to welcoming you.