Download Image
5.24 MB
ID # 171
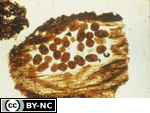
Fecal pellets of Oribatid mitesFrom the Soil Micromorphology Slide Collection
STEM Standard addressed: ESS2E - Biogeology
Appropriate Grade Level(s)
- College-level
- Classroom Lectures
- Laboratory Activities
- Soil Microbiology
Micromorphological description Of slide: Fecal pellets of Oribatid mites. Coarse micro and fine meso fecal pellets are weakly coalesced and very porous; they occur as loose infillings in cavities of decomposing plant fragments.
Data for the horizon
Horizon sampled: LFH
Depth sampled: 18-0 cm
Physical and chemical data available: L-H: OC = 48.5%, N = 1 .80%, pH = 7.2, TEC (cmol (+)/kg) = 138.6. FH: C = 39.4%, N = 2.20%, pH = 6.9, TEC (cmol (+)/kg) = 140.7. H: OC = 41 .1%, N = 2.40%, pH = 6.6, TEC (cmol (+)/kg) = 159.9
Macromorphological description of horizon: L-H (18-13 cm): Dark brown (7.5 YR 3/2 m) partially decomposed Populus balsamifera leaves, with a few partially decomposed roots; abundant medium fine and very fine random and horizontal roots. F-H (13-5 cm): Dark reddish brown (5 YR 3/3 m) humified and partially humified organic matter; loose and fluffy; abundant coarse and medium horizontal, fine and very fine random roots. H (5-0 cm): Dark reddish brown (5 YR 2/2 m) humified organic matter; loose; abundant coarse and medium horizontal, fine and very fine random roots.
Micromorphological description Of horizon: The F layer has mull-humiphytogranic fabric comprising comminuted plant fragments and an abundance of humigranic units ranging in size from 35vm to 950vm size are also common. Large (400-600vm) mullgranic units are concentrated in horizontal zones that resemble mull-like moder. The H layer is characterized by humigranoidic fabric of coalesced units dominantly 24-40vm and commonly 120-180pm in size. Phytogranic and orthogranic components are relatively few.
Data for thin section
Preparation of sample: Air dry
Impregnating medium: Epoxy
Thickness of section: 30 µm
Orientation of section: Vertical
Soil Classification
U.S.: Aquic Cryoboralf
F.A.O.: Gleyed Chernozem
Canada: Gleyed Black Chernozemic
Elevation: 700 m above sea level
Topography and hill slope position: Level to undulating Parent material: Lacustrine
Soil climatic data and/or soil water balance: Cold, subhumid soil climate
Vegetation: Balsam poplar (Populus balsamifera); aspen poplar (P. tremuloides); dogwood (Cornus stolonifera)
Data for the horizon
Horizon sampled: LFH
Depth sampled: 18-0 cm
Physical and chemical data available: L-H: OC = 48.5%, N = 1 .80%, pH = 7.2, TEC (cmol (+)/kg) = 138.6. FH: C = 39.4%, N = 2.20%, pH = 6.9, TEC (cmol (+)/kg) = 140.7. H: OC = 41 .1%, N = 2.40%, pH = 6.6, TEC (cmol (+)/kg) = 159.9
Macromorphological description of horizon: L-H (18-13 cm): Dark brown (7.5 YR 3/2 m) partially decomposed Populus balsamifera leaves, with a few partially decomposed roots; abundant medium fine and very fine random and horizontal roots. F-H (13-5 cm): Dark reddish brown (5 YR 3/3 m) humified and partially humified organic matter; loose and fluffy; abundant coarse and medium horizontal, fine and very fine random roots. H (5-0 cm): Dark reddish brown (5 YR 2/2 m) humified organic matter; loose; abundant coarse and medium horizontal, fine and very fine random roots.
Micromorphological description Of horizon: The F layer has mull-humiphytogranic fabric comprising comminuted plant fragments and an abundance of humigranic units ranging in size from 35vm to 950vm size are also common. Large (400-600vm) mullgranic units are concentrated in horizontal zones that resemble mull-like moder. The H layer is characterized by humigranoidic fabric of coalesced units dominantly 24-40vm and commonly 120-180pm in size. Phytogranic and orthogranic components are relatively few.
Data for thin section
Preparation of sample: Air dry
Impregnating medium: Epoxy
Thickness of section: 30 µm
Orientation of section: Vertical
Soil Classification
U.S.: Aquic Cryoboralf
F.A.O.: Gleyed Chernozem
Canada: Gleyed Black Chernozemic
Elevation: 700 m above sea level
Topography and hill slope position: Level to undulating Parent material: Lacustrine
Soil climatic data and/or soil water balance: Cold, subhumid soil climate
Vegetation: Balsam poplar (Populus balsamifera); aspen poplar (P. tremuloides); dogwood (Cornus stolonifera)
Method
Data for 35-mm slide
Frame length: 0.9 mm
Light mode: Plane polarized
Frame length: 0.9 mm
Light mode: Plane polarized
References
Sanborn, P. and S. Pawluk. 1983. Process studies of a Chernozemic pedon, Alberta (Canada). Geoderma 31 :205-237.
Pawluk, S. 1985. Soil micromorphology and soil fauna: Problems and importance. Quaest. Ent. 21 :473-497. (Publ. Dept. of Entomology, Univ. of Alberta, Canada, T6G 2E3)
Source: S. Pawluk
Slide BF27. Soil Science Society of America, 1993. A Reference Slide Collection for Soil Micromorphology. SSSA, Madison, WI.
Pawluk, S. 1985. Soil micromorphology and soil fauna: Problems and importance. Quaest. Ent. 21 :473-497. (Publ. Dept. of Entomology, Univ. of Alberta, Canada, T6G 2E3)
Source: S. Pawluk
Slide BF27. Soil Science Society of America, 1993. A Reference Slide Collection for Soil Micromorphology. SSSA, Madison, WI.
Peer Review: Yes
Credit this item to: SSSAMedia Date: 1993-01-01
Provided By: (SSSA) Soil Science Society of America
Author(s)/Creator(s)
-
* Soil Science Society of America
SSSA
Submitted By: (SSSA) Soil Science Society of America
Keywords
- Biological Features
- LFH Horizon
- micromorphology
- Orbatid mites
Comments
Please login to submit a comment.
Log In to your account
Already a member, certified, or existing customer?*
* Cookies must be accepted to log in.
Not sure if you have an account?
Check Your Email
Join Us!
Connect with members and access the information you need.
Learn more.
Ready to Join?
If you have an account, login on the left. Not sure if you have an account or need to create one? Check your email with the link above. We look forward to welcoming you.